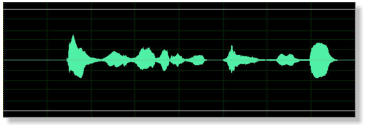
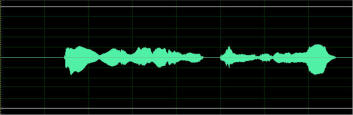
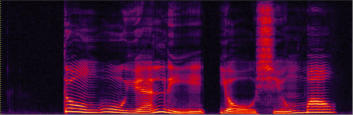
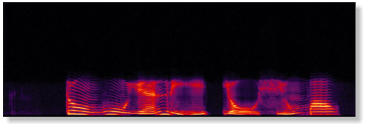
Telephone speech training module is designed to improve the recognition performance of
bandlimited speech (telephone speech) for hearing impaired listeners. This module is similar to the
basic module except that the frequency range of all acoustic sounds is limited to telephone
bandwidth (300-3200 Hz). Here shows the example of original and telephone bandlimited waveform
and spectrum.
The training groups in this module include:
Group 1: Pure Tones – practice identifying different pitches
Pure tones within the frequency range of 300-3200 Hz are not affected. Any pure tones
out of this range will be severely attenuated. Some listeners may not be able to hear
any sounds outside of this range. Some performance degradation is expected with this
training group. Since some sounds are highly attentuated, the training is designed to help the listener recognize
very soft sounds.
Group 2: Environmental Sounds – practice identifying common environmental
sounds
There will be little change in one’s ability to recognize environmental sounds that have
limited high frequency components. However, recognition performance of those
environmental sounds that include high frequency components will be significantly
reduced. It is expected that overall recognition performance will be reduced with
bandlimited. The training will help the listener focus on the available spectral cues and
discriminate different sounds with limited spectral information.
Group 3: Male/Female Identification - practice discriminating between speakers
Recent studies have shown that the voice gender recognition can be significantly
affected by bandliming (Horng et al., Ear and Hearing, 28(2), Suppl. 66S-69S). Loss of
high frequency information weakens the spectral contrast and results in lower
recognition performance. The training will aid the listener to focus on the periodicity cue
to discriminate voice gender and improve overall voice gender recognition performance.
Group 4: Vowel Recognition - practice vowel discrimination and identification
Vowel recognition is highly dependent on the F1 and F2 formant frequencies. Since
these are within telephone bandwidth, vowel recognition performance is not
significantly affected by bandlimiting for English. However, vowel recognition
performance is significantly reduced with telephone speech for other languages such
as Chinese. One reason is that some Chinese vowels are dependent on the spectral
difference in the high frequency region (e.g., YI versus YU). The loss of high frequency
information makes it difficult to discriminate these vowels in the Chinese language.
Group 5: Consonant Recognition - practice consonant discrimination and
identification
Consonant recognition is highly dependent on high frequency components. The loss of
high frequency components in bandlimiting speech may significantly reduce the
recognition performance of consonants. The training will help the listener to utilize other
available cues to discriminate different consonants.
Group 6: Word Discrimination – practice common words from four different topic
categories
Word recognition will be affected by the loss of high frequency components with
telephone speech since words generally include both vowel and consonant segments.
Since English vowel recognition is not affected by telephone bandwidth, performance
will be more dependent on consonants. Some words will be more affected by
bandlimiting than others. The training will aid the listener to utilize the available spectral
cues to discriminate different words.
Group 7: Everyday Sentences – practice identifying sentences with different
levels of background noise
Sentence recognition is one of the listening tasks which will be most affected by
bandlimits. Recent studies show a near 20% drop in recognition performance with
limited bandwidth [Fu, Q.-J. and Galvin, J.J. III (2006). “Recognition of Simulated
Telephone Speech by Cochlear Implant Patients,” Am J Audiol. 15(2), 127-132]. The
training will aid the listener to utilize available spectral cues to understand sentences.
Group 8: Music Appreciation – practice identifying musical instruments and
familiar tunes to aid music appreciation
Some musical instruments and familiar tunes may not be affected by bandlimiting if
their frequency ranges are primarily within the 300-3200 Hz. Otherwise, recognition
performance will be impacted by the bandlimits.